Infrastructures and facilities at Leibniz-Institut für Pflanzengenetik und Kulturpflanzenforschung in Gatersleben, IPK

For further information and Access please contact the following persons:
Thomas Altmann, Prof. Dr. altmann@ipk-gatersleben.de or
Astrid Junker, Dr. junkera@ipk-gatersleben.de
The different infrastructure equipment is catagorized into following groups:
Technology Platform Shoot
High throughput plant phenotyping systems
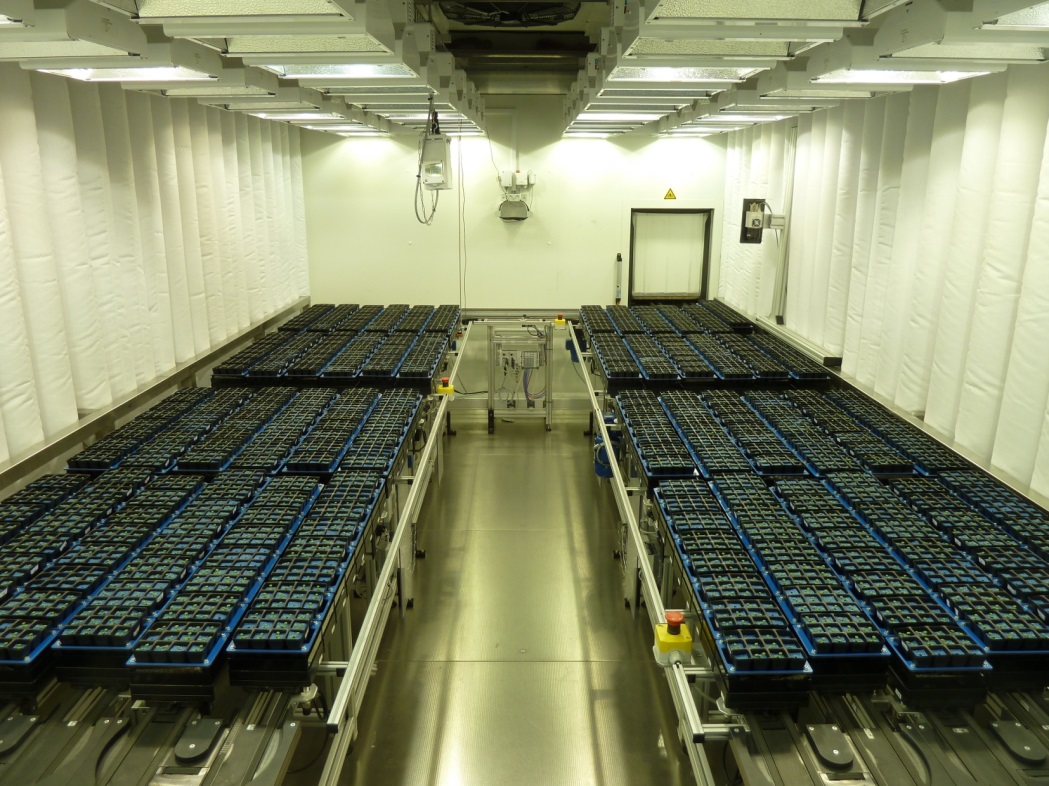
small plants |
medium plants | |
|---|---|---|
 |  | |
| more details | more details | |
| Location of the facility | Climatized phytochamber | glasshouse |
| Screening object | Whole plant | Whole plant |
| Capacity | 384 – 4608 plants | 520 plants |
| Plant size/spezies | Maximal plant width: 30 cm Maximal plant height: 140 cm e.g. Hordeum vulgare | Maximal plant width: 30 cm Maximal plant height: 140 cm e.g. Hordeum vulgare |
| Method | fluorescence imaging (excitation: 400-500 nm, emission: 520-750 nm), visible imaging (390-750 nm), and near infrared imaging (1450-1550 nm) | fluorescence imaging (excitation: 400-500 nm, emission: 520-750 nm), visible imaging (390-750 nm), and near infrared imaging (1450-1550 nm) |
| Traits/parameters to be measured | plant architectural traits (plant height and width, projected leaf area (top, side view), estimated volume), physiological traits (color-related, CHL fluorescence, relations to moisture content by NIR) | plant architectural traits (plant height and width, projected leaf area (top, side view), estimated volume), physiological traits (color-related, CHL fluorescence, relations to moisture content by NIR) |
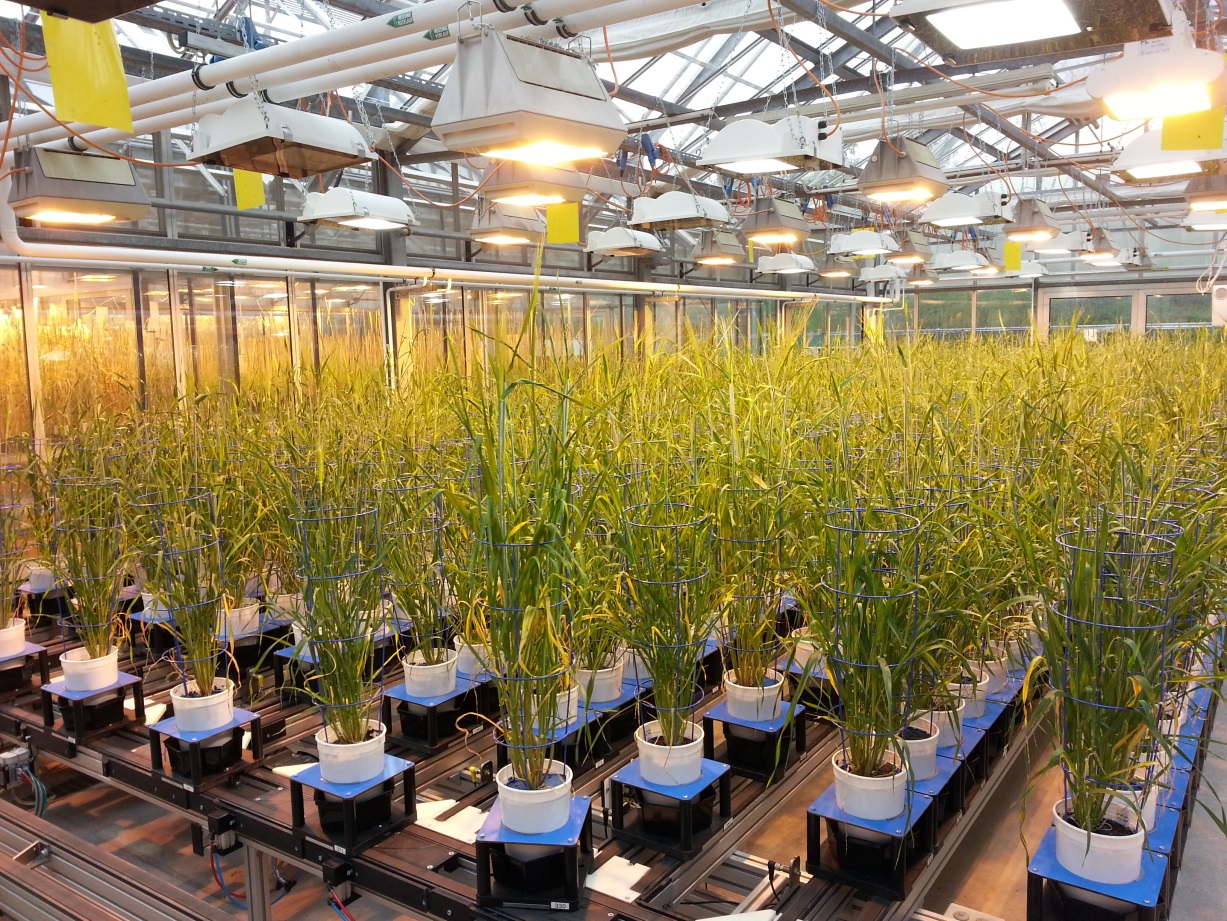
large plants |
Phenobot (System under development) | |
|---|---|---|
 |  | |
| more details | more details | |
| Location of the facility | glasshouse | GH, stationary (relocation possible) |
| Screening object | Whole plant | leaf surface (trichomes), automated selection of representative leaf areas |
| Capacity | 396 - 1584 plants | Approx. 90 plants per day |
| Plant size/spezies | Maximal plant width: 70 cm Maximal plant height: 230 cm e.g. Zea mays | Rosette type plants, single stem plants, grasses (e.g. Arabidopsis, tobacco, barley) |
| Method | fluorescence imaging (excitation: 400-500 nm, emission: 520-750 nm), visible imaging (390-750 nm), and near infrared imaging (1450-1550 nm) | Imaging |
| Traits/parameters to be measured | plant architectural traits (plant height and width, projected leaf area (top, side view), estimated volume), physiological traits (color-related, CHL fluorescence, relations to moisture content by NIR) | Trichomes per area, trichome types (still in testing stage) |
Technology Platform Patho
Micro- and Macrophenomics facilities for plant-pathogen interactions
Accurate description of the initial stages on infection by microbial pathogens inevitably requires microscopic techniques. Too meet the challenge of merging these techniques with the high-throughput requirements of a phenomics screen we have developed the Microphenomics platform. It combines high-throughput DNA cloning, single cell transformation protocols, and automated microscopy and image analysis. It was used successfully to address the function of genes in nonhost- and race-nonspecific host resistance of barley interacting with the powdery mildew fungus Blumeria graminis.
Additional phenomics tools aiming to cover the complete asexual interaction cycle of powdery mildew fungi with barley, and to allow quantitative assessment of disease symptoms and host responses are also in progress.
The barley/barley powdery mildew (Blumeria graminis f.sp. hordei) and wheat/wheat powdery mildew (Blumeria graminis f-sp. tritici) are currently the most well established of our patho-systems. Barley/spot blotch (Bipolaris sorokiniana) and Arabidopsis thaliana/Arabidopsis powdery mildew (Golovinomyces orontii) are available as well.

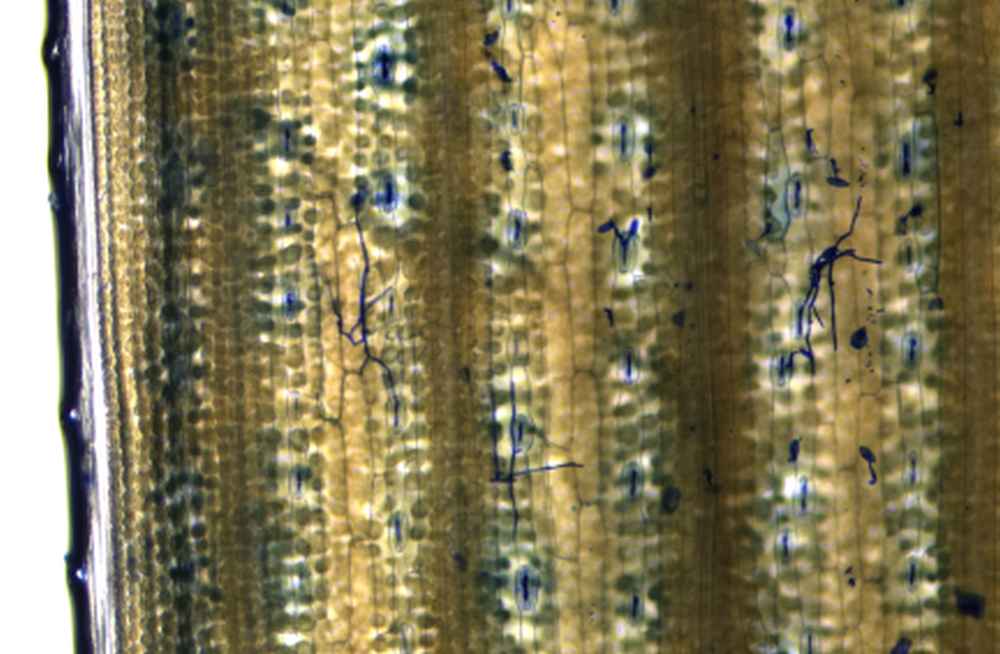
Microphenomics facility |
Macrophenomics facility | |
|---|---|---|
 |  | |
| more details | more details | |
| Location of the facility | IPK, Genome Center building | IPK, Genome Center building |
| Screening object | Detached leaves | Detached leaves |
| Capacity | Up to 80 RNAi target genes/week; up to 300 genotypes/week | Up to 500 genotypes/experiment (3-4 weeks) |
| Plant size/spezies | Plants: H. vulgare, T. aestivum, A. thaliana Pathogens: B. graminis, G. orontii | Plants: H. vulgare, T. aestivum, A. thaliana Pathogens: B. graminis, B. sorokiniana, G. orontii |
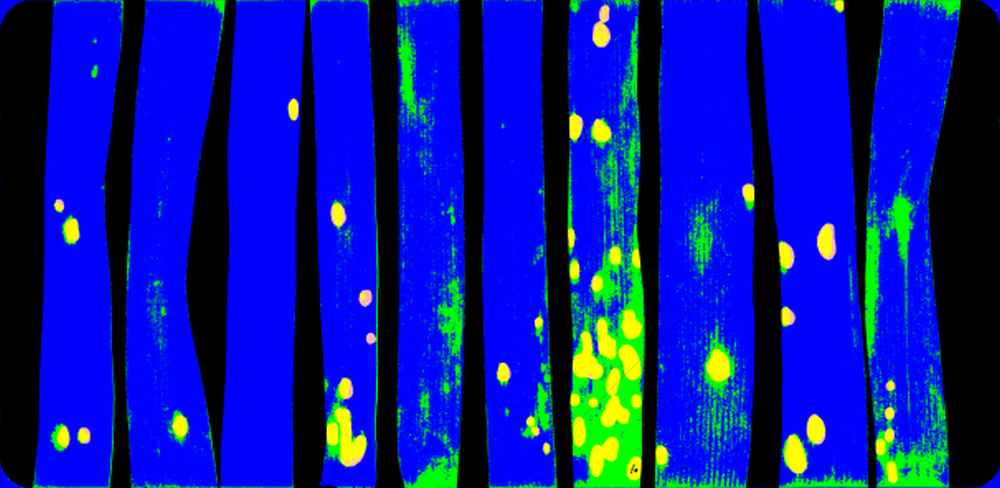
| Method | Microscope imaging | Multispectral imaging (365-850 nm) |
| Traits/parameters to be measured | Fungal penetration efficiency; fungal hyphae growth | Fungal colonies/leaf area; Colony area; Plant responses (melanization, epifluorescence) |
Technology Platform Field
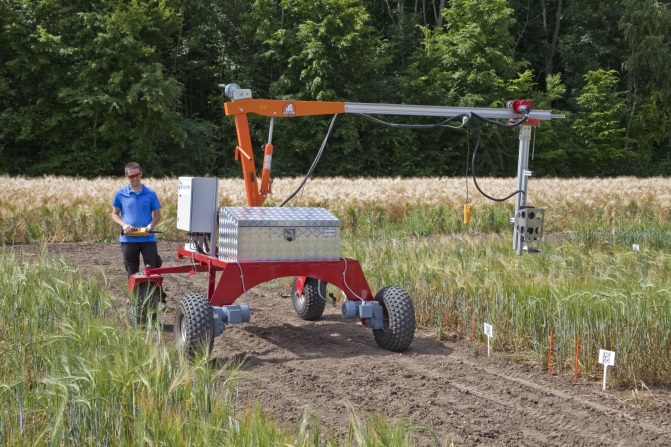
AgRover | |
|---|---|
 | |
| more details | |
| Location of the facility | Fields or experimental field plots Readily transported between sites |
| Screening object | Field plots/whole plants |
| Capacity | ~ 3 km/day (eg. ~ 600 x 5 m plots) |
| Plant size/spezies | Any plant to a maximum height of 60-80 cm |
| Method | Hyperspectral imaging (1000 - 2500µm) of plants from above or from the side. |
| Traits/parameters to be measured | Physiological status (eg. nutrient content) Root depth (indirectly) |
